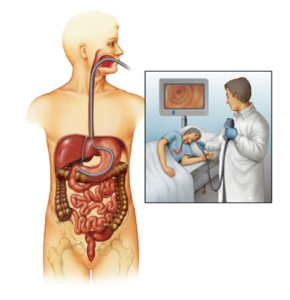
OGD SCOPY/UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY
Best gastroenterologist doctor in kalyan
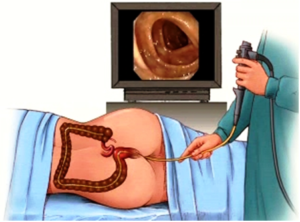
UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY OR OGD SCOPY IS A MINIMALLY INVASIVE PROCEDURE TO INVESTIGATE AND TREAT PROBLEMS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. IT IS BOTH IDAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE DONE UNDER LOCAL OR SEDATION. IT IS USED TO TREAT OESOPHAGEAL VARICES, STRICTURES, ULCER BLEEDS AND HIATAL HERNIA.
Upper GI endoscopy (sometimes called a ‘gastroscopy’ or simply an ‘endoscopy’) is a test which allows the doctor to assess the food pipe the stomach and around the first part of the small intestine – the duodenum. A small tube with camera is passed through your mouth into the stomach. Looking thru the tube, we get a clear view of the stomach. Sometimes the doctor takes sample of tissue for analysis in the laboratory.
Preparation before the procedure
You will be asked not to have anything to eat or drink for at least five to six hours before the test. When you come to the department, a doctor will explain the test to you and will usually ask you to sign a consent form. If you have any questions at this stage don’t be afraid to ask. It will also be necessary for you to remove any false teeth. They will be kept safely until after the examination.
During the test
In the examination room you will be made comfortable on a couch, resting on your left side. A nurse will stay with you throughout the test. Some doctors may spray a local anaesthetic on the back of your throat or give you a tablet to suck to numb the area. To keep your mouth slightly open, a mouthpiece will be put gently between your teeth. The procedure will be a painless one. During this time some air will be passed down the tube to distend the stomach and allow the doctor a clearer view.
After the test
You will be left to rest in the unit for at least thirty minutes. After this you can eat and drink normally. The back of your throat may feel sore for the rest of the day. You may also feel a little bloated if some of the air has remained in your stomach. Both these discomforts will pass, and need no medication.